Male Breast Reduction
-
 Medically Reviewed by Charlie Chen, MD | Last updated 10/18/2023
Medically Reviewed by Charlie Chen, MD | Last updated 10/18/2023 - Overview
Overview
What is male breast reduction?
Male breast reduction, also known as gynecomastia surgery removes excess fat in the chest and problematic glandular tissue. This procedure can also reduce the size of the areolas and nipples. The goal of male breast reduction surgery is to make the chest flatter, firmer and more masculine.
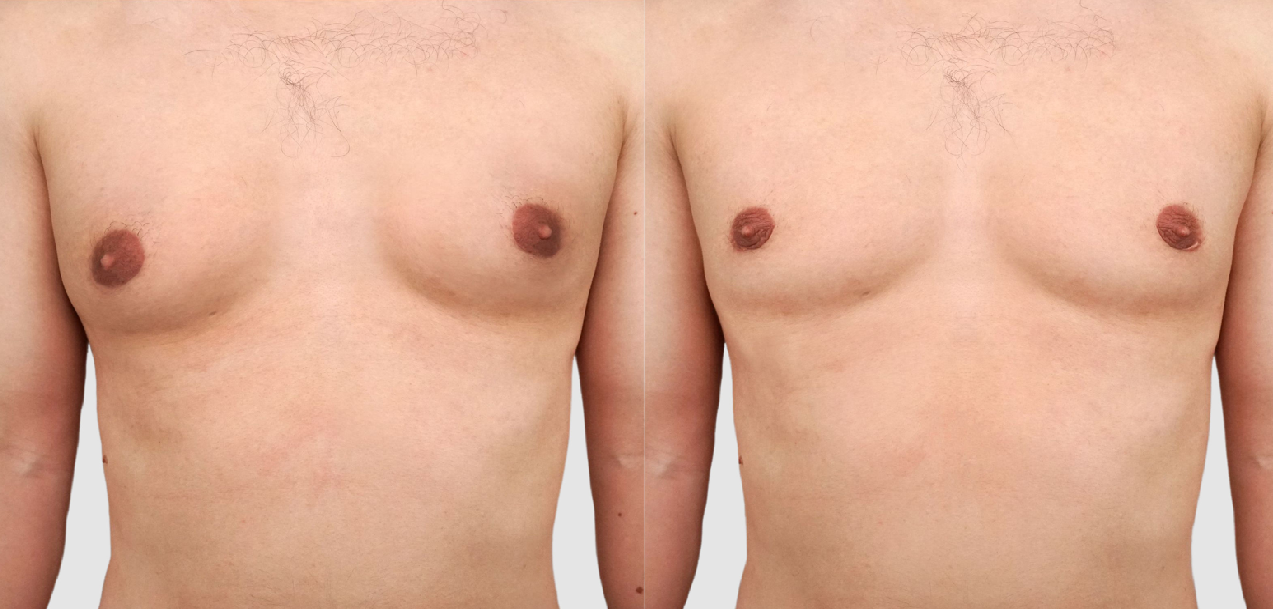
Gynecomastia Before & After Photo
Topics covered on this page
- Cost of male breast reduction
- Is the cost covered by insurance?
- What exactly is gynecomastia?
- Gynecomastia vs. pseudogynecomastia
- Causes of male breasts
- Is surgery right for you?
- What men should know beforehand
- Procedure options
- Recovery time
- When to expect results
- How long will results last?
- Non-surgical alternatives
- Tips for choosing a plastic surgeon
Cost of male breast reduction
The average cost of male breast reduction surgery is $4,239 according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), however this is only the surgeon’s fee. There are several other factors that can affect the cost of your procedure. Here are some of the top factors that can influence cost.
- Your Surgeon: The experience and reputation of the plastic surgeon performing your procedure can affect the cost. Highly skilled male breast reduction surgeons often charge a premium for their services.
- Anesthesia: The administration of anesthesia involves the expertise of an anesthesiologist. The type of anesthesia used, the duration of the procedure, and the qualifications of the anesthesia provider influence the anesthesia fees.
- Surgical Facility: The surgical facility where your male breast reduction is being performed may impact the cost. These fees cover the usage of the operating room and other associated services. To ensure a safe experience, check to see if your surgical facility is certified by the Accreditation Associations for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC).
- Location Matters: The cost of living and the average pricing for medical services in a particular area can affect the cost of your procedure. In general, urban areas tend to have higher procedure fees. If you want to get a rough idea of the prices for medical procedures in your local area, you can use the Healthcare Blue Book, which functions similarly to Kelley Blue Book for estimating car prices.
- Technique Used: Different surgical techniques such as extensive tissue excision or liposuction may have varying costs.
- Complexity of the Procedure: The complexity of your procedure can affect the cost. If it involves significant reconstruction or additional procedures expect the cost to be on the higher side
- Pre and Postoperative Care: This includes consultations, medical tests, surgical garments, medications, and follow-up appointments.
- Insurance: In certain cases, your procedure may be covered by insurance if it is deemed medically necessary. In these cases, insurance may cover a portion of the procedure. However, insurance coverage can vary and specific criteria must be met to qualify.
When taking all these factors into consideration, the total cost of male breast reduction surgery can range from $7,500 to $15,000.
If you are considering male breast reduction, setup a consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon near you. This will allow you to discuss your aesthetic goals and gain a better understanding of the specific costs involved.
Is the cost covered by insurance?
In most cases, male breast reduction surgery is not covered by insurance. However, there may be exceptions for cases of persistent gynecomastia (glandular breast tissue) that cause pain or discomfort. Pseudogynecomastia (fatty breast tissue) is typically not covered by insurance.
Regardless of the type of tissue, male breast reduction surgeries are generally not covered when they are performed to improve mental health and emotional well-being. Cases where surgery may be covered include:
- Documented endocrine disorders
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Persistent, painful adolescent onset gynecomastia
Insurance companies that cover male breast reduction will often require photographic documentation, preoperative tests to confirm the presence of glandular breast tissue, and laboratory tests to rule out hormonal imbalances.
To see if you qualify for male breast reduction coverage, contact your insurance provider directly.
What is gynecomastia?
Overdeveloped breasts in men, or gynecomastia, is not uncommon. By some estimates, up to 65% of men will meet criteria for enlarged breast tissue on one or both sides of their chest at some point in their lifetime. Although it is often benign, gynecomastia can be uncomfortable and embarrassing and may cause psychological distress, body dysmorphia, and depression. Gynecomastia may also be indicative of a serious underlying health problem. If you are concerned by enlarged breasts, see your doctor to rule out serious health issues.
Gynecomastia vs pseudogynecomastia
There are two types of tissue that may be involved with enlarged breasts. Glandular tissue is involved in hormonal regulation and requires tissue excision while excess adipose tissue (fat) can often be addressed with liposuction.
- Gynecomastia is caused by excessive breast glandular tissue in men, which is a normal type of tissue that is involved in hormonal regulation
- Pseudogynecomastia indicates excessive adipose tissue (fat) and is often associated with high body fat content; additionally, men who have lost substantial amounts of weight are often frustrated by persistent pseudogynecomastia
In some cases, both gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia are present simultaneously.
How to tell if it’s caused by fatty tissues or breast tissues? In many cases, you can differentiate between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia by how the excess breast tissue feels. Homogeneously soft breast tissue is likely indicative of pseudogynecomastia, while firm or hard tissue suggests gynecomastia. A physician can conclusively determine whether you have gynecomastia, pseudogynecomastia, or a combination of both.
Causes of male breasts
Enlarged breasts in men is the result of an imbalance in the hormones testosterone and estrogen. An increase in estrogen or a decrease in testosterone can trigger the development of breast tissue in men. There are a number of factors that can contribute to hormonal imbalance, including:
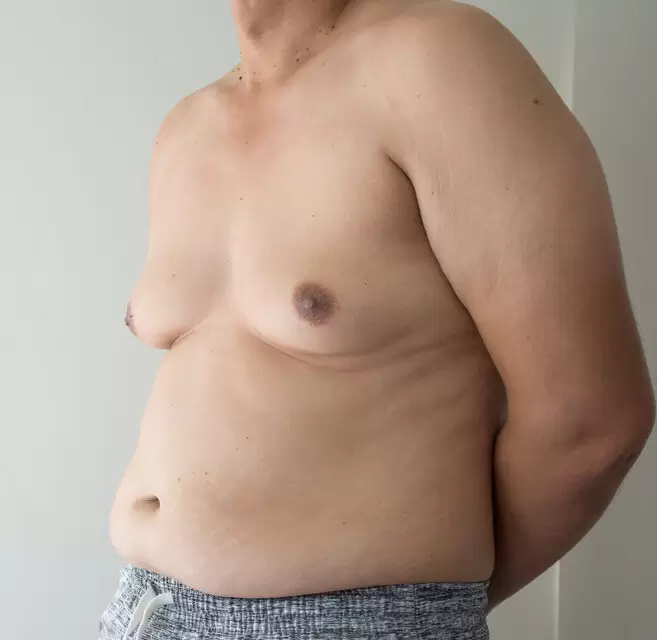
Male with Gynecomastia (Man Boobs)
- Environmental chemicals or pollutants
- Prescription medications
- Recreational drugs (including anabolic steroids)
- Vitamin or mineral deficiencies or calorie malnutrition
- Testosterone deficiency
- Age (adolescents and men over the age of 50 are at the highest risk for gynecomastia)
- Genetics (especially Klinefelter syndrome)
- Overactive thyroid gland or other endocrine disorders
- Metabolic disorders
- Liver or kidney problems
- Tumors
If you are concerned about overdeveloped breasts, the first thing to do is to make an appointment with your doctor to determine the exact cause. In rare cases, enlarged breast tissue in men is indicative of a serious health issue that should be addressed quickly.
Is surgery right for you?
You might be a good candidate for male breast reduction if you are:
- Healthy and emotionally stable
- Within your ideal body weight
- Affected by gynecomastia on one or both breasts
- Over 18 years old. Teens are advised to wait until after puberty as the breasts may still be developing
- Have good skin elasticity
You may not be a good candidate if you are:
- Unhealthy, or have serious medical conditions making you unfit for surgery
- Unrealistic about what to expect
- Mentally unstable
In order to undergo a safe and effective male breast reduction surgery, you will need to provide your surgeon with a complete medical history. This will allow your surgeon to determine the cause of gynecomastia as well as identify health concerns that may need additional treatment.
For example, impaired liver function may contribute to gynecomastia and may also be indicative of an underlying health problem that, if not treated, may lead to a recurrence of breast tissue development post-surgery.
It is important to be honest about any recreational use of prescription or illicit drugs. Anabolic steroids, marijuana, and excessive alcohol use may contribute to male breast development.
What men should know beforehand
- In rare cases, gynecomastia may return after male breast reduction surgery. This may be caused by incomplete removal of excess glandular tissue, untreated medical issues, or an unhealthy lifestyle. The best way to prevent gynecomastia recurrence is to work with an experienced surgeon and to maintain a healthy lifestyle after the operation.
- Male breast reduction surgery will leave a small scar in the lower part of the areola (nipple area), and liposuction can leave tiny scars in the armpit or on the chest. In most cases, any scars will be inconspicuous. Make sure to discuss potential scarring with your surgeon during your consultation.
- Although results of the surgery will be apparent immediately, it will take several months before final results can be fully appreciated.
Procedure options
The surgical procedure to remove excess male breast tissue will vary depending on the type of tissue that is causing breast development. In some cases, liposuction alone is sufficient to achieve the desired results. In other cases tissue excision with or without liposuction is required. Common surgical methods used to treat gynecomastia include:
- The Webster Incision: This is one of the most common methods used to treat gynecomastia. A small incision (~1 inch) is made in the pigmented periareolar skin underneath the nipple and excessive glandular tissue is excised. This method can be combined with liposuction.
- The Minimally Invasive Method: In this method, a very small (~5 mm) incision is made at the edge of the nipple, allowing for both liposuction and glandular tissue excision to be performed. This method leaves the smallest scar.
- Ultrasonic Liposuction Method: Ultrasonic liposuction is a technique that liquifies fat cells prior to liposuction, making it more effective than traditional liposuction. This method is appropriate for cases of pseudogynecomastia (fatty tissue) but cannot remove excess glandular breast tissue associated with gynecomastia. Ultrasonic liposuction can be used with either of the above techniques and is often done in conjunction with glandular tissue removal.
Recovery time

Compression garment photo courtesy of www.NouvelleInc.com
Recovery times will differ between individuals, but most people are able to return to work or school within 5-10 days after the surgery.
Your doctor may recommend you wear a compression garment over the chest area for at least one to two weeks. Elastic compression garments reduce swelling and result in a shorter recovery period. This garment supports the tissues in their new position, helping the skin adjust to its new contours and reducing the possibility of skin looseness.
It is imperative that you carefully follow all directions provided to you by your surgeon in order to minimize recovery time and achieve the best long-term results.
When to expect results
Initial results will be apparent immediately following the surgery, but final results will take 3-6 months to become fully visible.
How long will your results last?
Male breast reduction surgery results often last for a lifetime in people who maintain a healthy lifestyle. Rarely, a recurrence of gynecomastia can occur after male breast reduction surgery. The most common cause of recurrence is incomplete removal of glandular tissue.
Non-surgical alternatives
Gynecomastia caused by excess glandular tissue can only be effectively treated with surgery. However, for pseudogynecomastia which is associated with excess fat, there are several treatment options to consider. The first involves weight loss through exercise and a healthy diet. Other non-surgical options that may reduce breast size in men with pseudogynecomastia include:
- Radiofrequency (VelaShape®)
- Ultrasound (UltraShape® Power)
- Radiofrequency plus ultrasound (Exilis Ultra™)
- Cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting®)
These techniques effectively break down fat cells, but since they do not physically remove the remnants of the fat cells, visible results are not seen immediately. Moreover, multiple sessions are usually required to achieve the desired outcome.
In most cases, non-surgical treatments for pseudogynecomastia have not proven to be as effective as liposuction.
Tips for choosing a plastic surgeon
It is important to carefully select your male breast reduction surgeon. The surgeon you choose can significantly impact your surgical outcome and overall satisfaction. Find a plastic surgeon with extensive experience in performing male breast reduction procedures. Also, make sure that they are board-certified and affiliated with one or more of the following organizations:
- The American Board of Plastic Surgery
- The American Society of Plastic Surgeons
- The Aesthetic Society
EnhanceMyself.com relies on sources such as professional medical organizations, government agencies, academic institutions, and peer-reviewed scientific journals to write it’s articles. Learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate, in-depth, and unbiased by reading our editorial guidelines.
*Medical Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. Read more.


