Chemical Peel
-
Content written by Andrew Proulx, MD | Reviewed by EnhanceMyself Medical Team | Last updated 6/12/2023
- Overview
Overview
What are chemical peels?
There may not be a fountain of youth, but there are a number of real-world anti-aging treatments that can help turn back time, leaving you feeling and looking more youthful and rejuvenated. One of the more popular anti-aging procedures available is skin resurfacing using chemical peels. Chemical peels – more formerly known as chemoexfoliation – involves applying caustic agents to the skin to ablate the skin to a desired depth in order to stimulate the regrowth of healthier, more youthful looking skin.
Cost of chemical peels
The average cost of chemical peels is $519 according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). However, the price can vary widely depending on a variety a factors, with the primary determinant being the type of chemical peel.
- Superficial or Light Peels: Superficial or light chemical peels are typically the least expensive option. They are milder peels that target the outermost layer of the skin. On average, the cost for superficial peels can range from $100 to $300 per treatment session.
- Medium Peels: Medium chemical peels penetrate deeper into the skin, targeting both the outer layer and the middle layer of the skin. They may address more significant skin concerns, such as acne scars, uneven pigmentation, or fine lines. Medium peels generally cost between $300 and $800 per treatment session.
- Deep Peels: Deep chemical peels are the most intensive and aggressive type of peel, reaching the deeper layers of the skin. They are typically used to address severe skin conditions, deep wrinkles, or substantial sun damage. Due to their complexity, deep peels often have higher costs, ranging from $800 to $5,000 per treatment session.
It’s important to note that multiple sessions may be recommended for optimal results, especially for medium and deep peels.
Factors affecting the cost of treatment
There are several factors can influence the cost of your chemical peel. Here are some of the most common factors that influence cost:
- Type of Chemical Peel: Different types of chemical peels vary in intensity and target different skin issues. Generally, superficial peels are less expensive than medium or deep peels.
- Location Matters: Where you live can impact the cost of chemical peels. Generally, healthcare expenses tend to be higher in urban areas and regions with a higher cost of living.
- Your Chosen Provider: The experience and reputation of the healthcare provider performing your chemical peel can affect the cost. Highly skilled providers often charge a premium for their services.
- Clinic or Facility: The setting in which the chemical peel is done can also affect the cost. Upscale clinics with advanced technology and luxurious amenities often charge more compared to simpler settings.
- Number of Treatment Sessions: Multiple treatment sessions may be required to achieve the desired results.
- Pre- and Post-Treatment Care: Properly preparing the skin before the peel and following post-treatment care instructions are crucial for optimal results. Costs may include skincare products or consultations provided by the clinic.
- Additional Treatments: In some cases, additional treatments may be recommended to enhance the overall results or address specific concerns.
It’s important to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional for an accurate cost estimate.
Are you a candidate?

People with a fair skin tone and light-colored hair often are excellent candidates, though that’s not always the case if you have other underlying considerations. If any of the following applies to you, you may not a candidate for chemical peel:
- You have red hair and pale freckled skin.
- You suffer from abnormal skin pigmentation.
- You are of Afro-Caribbean or Asian descent.
- You have facial warts.
- You are nursing or pregnant.
- You have a skin condition like eczema or psoriasis.
- You have used certain acne medications or certain other medications recently.
If you are considering a chemical peel, you should set up a consultation with a professional to evaluate your concerns and discuss your options. Your practitioner may wish to conduct a test-spot on your skin to test your reaction to a chemical peel agent.
What conditions can it treat?
Chemical peels are useful for treating four categories of skin concerns:
- Pigmentary disorders – such as melasma and age spots (solar lentigines)
- Inflammatory disorders – such as acne and rosacea
- Mild scarring – such as acne scarring, and scarring from trauma or surgery
- Aging effects – such as superficial and medium-depth fine lines (rhytides), and actinic keratoses (pre-cancerous sun-induced skin lesions).
Unfortunately chemical peels cannot be used to address all skin concerns, notably deep facial lines, severe scarring, skin sagging, or broken capillaries. Other facial treatments may be more appropriate for these types of issues.
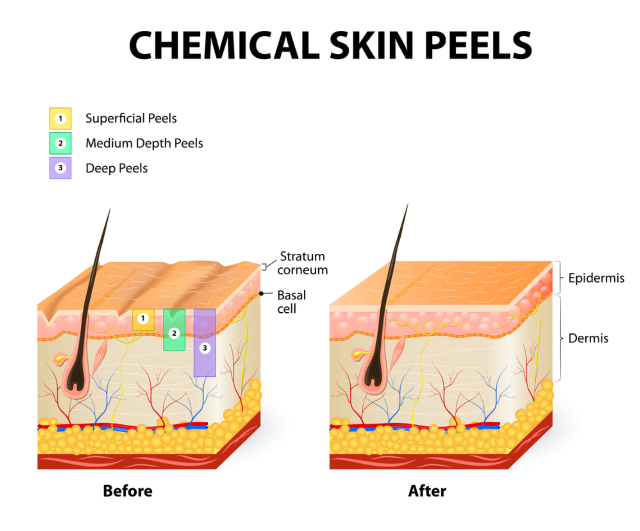
Types of chemical peels
There are a wide variety of different chemical peels available to choose from, typically identified by the strength of the agent used. Chemical peels are classified according to the depth of the wound that is created by the peel, as follows:
Light or superficial peel: these penetrate only the superficial aspect of the skin (the epidermis). This is sometimes referred to as a “lunchtime” peel because many people can return to normal daily activities soon after the treatment. Minor discoloration or rough skin are best treated with this basic peel approach.
- Medium peel: these penetrate the superficial layer and part of the underlying layer of skin (the epidermis into the papillary dermis). These are used for treating age spots, fine lines and wrinkles, and even some unwanted skin growths.
- Deep peel: The most aggressive approach to chemical peel, the deep peel is used to penetrate several layers of damaged skin (the epidermis, papillary dermis, and into the reticular dermis). Used for more stubborn scarring, skin discoloration, age spots, etc.
The depth of the peel is determined by a number of factors:
- The chemical agent
- The concentration of the agent (the same chemical agent in different concentrations will penetrate to different depths)
- Your skin type
- The number of layers applied (i.e. the depth of the “frosting”)
- The number of treatments applied, and the time between treatments
The most commonly used chemical agents include:
- Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) – such as glycolic acid or pyruvic acid
- Beta hydroxyl acids (BHAs) – such as salicylic acid or beta-lipohydroxy acid (LHA)
- Alpha keto acids (AKAs)
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
- Tretinoin – a vitamin A derivative
- Baker-Gordon phenol – a mixture of detergent, croton oil, phenol, and water
- Monheit’s combination – Jessner’s solution (salicylic acid, resorcinol, lactic acid, and ethanol)) mixed with TCA
- Coleman’s solution – glycolic acid mixed with TCA
Procedure
A chemical peel is an outpatient procedure, usually done in an office/clinic setting, and generally lasts only about 15-60 minutes. The procedure is relatively simple:
- Depending on the condition of your skin and the type of treatment, your practitioner may ask you to pre-treat your skin with a pre-peel solution starting 2-4 weeks prior to and stopping 3-5 days before the treatment.
- On the day of the treatment, your skin is prepared by using a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, debris, make-up, and sunscreen. The skin is then thoroughly de-greased and debrided using a more aggressive cleanser (such as acetone or an alcohol).
- The patient is positioned and vulnerable areas (the inner corners of the eyes and the crease of the nose) are protected with petroleum jelly or gauze.
- The chemical peel agent is applied carefully to achieve the desired uniformity and thickness (known as the “frosting level”). The number of layers applied depends on the agent used and the desired depth of ablation.
- After the desired depth of ablation is achieved, the peel agent is neutralized by applying a sodium bicarbonate solution followed by cool saline compresses. Some peel agents are self-neutralizing and do not require this step.
Recovery time
After your treatment, you will be asked to continue to apply cold compresses, an emollient (such as mineral oil or a moisturizer) and sunscreen.
For the first 24 hours, gentle cleansing with diluted vinegar (acetic acid) four times a day is recommended in order to prevent infection. This is followed by application of an emollient.
After the first 24 hours, care involves routine cleansing with a gentle cleanser followed by application of an emollient. Aggressive sun-blocking with sunscreen and broad-brimmed hats and sun avoidance is required until healing is complete.
Following a chemical peel, you can expect redness, swelling, and peeling skin to continue for 1-3 days for a superficial peel, and 5-10 days for a deeper peel. You must resist the temptation to scratch, pick at, or peel the treated area.
When will you see results?
Recovery time varies, but it typically takes one to three weeks before your results are fully realized. Depending on what you hope to achieve, you may require multiple treatment sessions. Results can last several months before the signs of aging begin to resurface. Ongoing sunscreen use is important for maintaining results.
Does it hurt?
Unfortunately there is no simple answer to that question because everyone has a different pain threshold. Naturally, you are stripping away a layer of skin using caustic agents, so there is some level of discomfort involved.
Pain management is accomplished through the use of fans, cold packs, and oral medications such as acetaminophen or anti-inflammatories.
Generally, anesthesia is not used, although some practitioners may use a local anesthetic, or – uncommonly – a general anesthetic. The use of phenol sometimes necessitates sedation and anesthesia.
Some discomfort and burning are common for 2-5 days following medium and deep peels in people with sensitive skin. Sometimes the sunscreens used post-treatment can sting.
For more information on chemical peels visit www.aad.org.
EnhanceMyself.com relies on sources such as professional medical organizations, government agencies, academic institutions, and peer-reviewed scientific journals to write it’s articles. Learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate, in-depth, and unbiased by reading our editorial guidelines.
*Medical Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. Read more.

 Light or superficial peel: these penetrate only the superficial aspect of the skin (the epidermis). This is sometimes referred to as a “lunchtime” peel because many people can return to normal daily activities soon after the treatment. Minor discoloration or rough skin are best treated with this basic peel approach.
Light or superficial peel: these penetrate only the superficial aspect of the skin (the epidermis). This is sometimes referred to as a “lunchtime” peel because many people can return to normal daily activities soon after the treatment. Minor discoloration or rough skin are best treated with this basic peel approach.

